Lung Cancer CT Scan: An In-Depth Overview for Patients
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. The early detection of lung cancer can significantly increase survival rates, making diagnostic tools, such as the lung cancer CT scan, crucial in modern medicine. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding what a lung cancer CT scan is, how it works, and its role in the broader spectrum of health and medical care, particularly in the fields of sports medicine and physical therapy.
Understanding Lung Cancer
Lung cancer occurs when cells in the lungs grow uncontrollably, leading to the formation of tumors. The two main types are:
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): The most common type, accounting for about 85% of cases.
- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC): A more aggressive type that tends to spread quickly.
Common risk factors include:
- Tobacco use: Smoking is the primary risk factor for lung cancer.
- Secondhand smoke: Exposure can increase risk even for non-smokers.
- Environmental factors: Radon exposure, asbestos, and pollution can contribute to the risk.
The Role of CT Scans in Diagnosing Lung Cancer
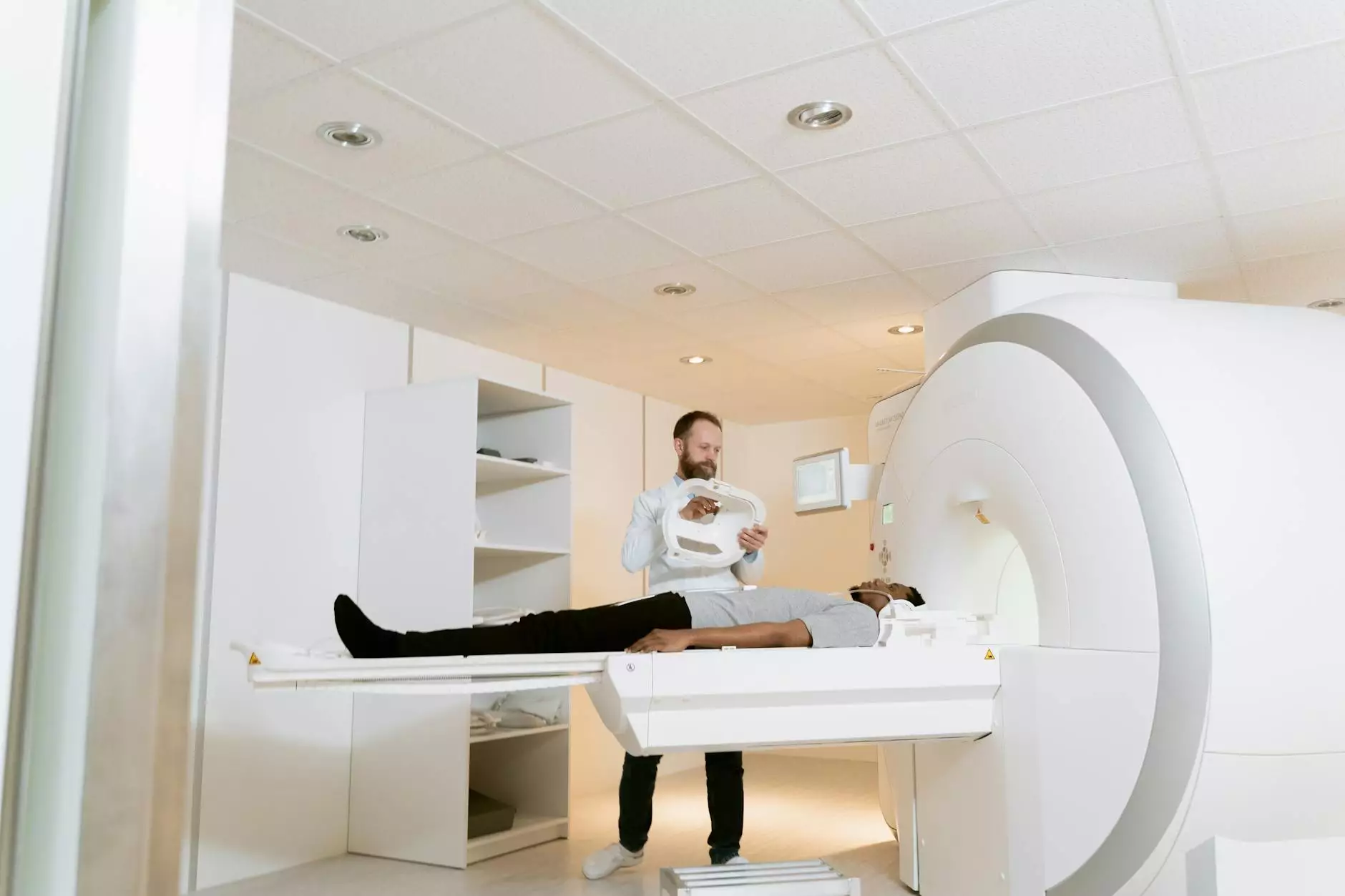
A CT scan, or computed tomography scan, is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. Here’s how it plays a vital role in lung cancer diagnosis:
What is a Lung Cancer CT Scan?
A lung cancer CT scan specifically focuses on the lungs and surrounding areas. Unlike standard X-rays, CT scans offer greater clarity and provide more information about lung structures. They can help detect abnormalities in the lungs, such as:
- Tumor presence and size
- Lymph node involvement
- Status of surrounding tissues
How Does a CT Scan Work?
The CT scanning process involves the following steps:
- Preparation: Patients may be asked to avoid food and drink for a few hours before the scan.
- Positioning: Patients lie down on a table that slides into the CT scanner. They may be positioned face up or down, depending on the area being scanned.
- Scanning: The scanner takes multiple X-ray images from different angles, which a computer assembles into cross-sectional images.
- Post-Procedure: After the scan, patients can usually resume normal activities immediately.
Benefits of CT Scans for Lung Cancer Detection
CT scans provide several benefits in the detection and management of lung cancer:
- Early Detection: CT scans can identify lung cancer at its earliest stages when it is most treatable.
- Precision: The detailed images allow for precise measurement of tumor size and the identification of subtle changes in lung tissue.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Alongside other diagnostic tools, CT scans help medical professionals develop a complete picture of the patient’s lung health.
Preparation for a Lung Cancer CT Scan
Preparing for a lung cancer CT scan is relatively straightforward, but certain steps are necessary to ensure accurate results:
- Consult Your Doctor: Discuss your medical history, current medications, and any allergies.
- Clothing: Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing; you may be asked to change into a gown.
- Metal Objects: Remove any jewelry, glasses, or metal objects that may interfere with imaging.
- Contrast Material: In some cases, patients may receive a contrast dye to enhance visibility; inform your doctor if you're allergic to iodine.
What to Expect During a CT Scan
During the scan, you can expect:
- Duration: Most scans take about 10 to 30 minutes.
- No Pain: The process is painless, but you may experience brief discomfort from lying still.
- Communication: Technicians will provide instructions, such as when to hold your breath.
Post-CT Scan Care and Follow-Up
After the CT scan, patients are generally allowed to leave without complications. However, follow-up is crucial:
- Review Results: Schedule an appointment to discuss the scan results with your healthcare provider.
- Possible Additional Tests: Depending on the findings, further tests, or biopsies may be required.
- Regular Monitoring: For high-risk patients or those with a history of lung issues, regular follow-ups may be necessary.
Integrating CT Scans in Health and Medical Practices
In the larger context of health and medical practices, the lung cancer CT scan is a critical component of a multidisciplinary approach. It integrates well with:
Sports Medicine
In sports medicine, where lung health can impact an athlete's performance, understanding respiratory conditions through CT imaging can aid in:
- Assessment: Evaluating respiratory health in athletes.
- Prevention: Identifying risks related to lung capacity and functionality.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapists may use CT scans to tailor rehabilitation programs for patients recovering from lung-related conditions by:
- Designing Targeted Therapies: Focusing on strengthening respiratory muscles.
- Improving Quality of Life: Helping patients regain functionality and manage symptoms.
The Future of Lung Cancer Detection and Diagnosis
As technology advances, the future of lung cancer detection looks promising. Emerging technologies and improvements in imaging will lead to:
- Enhanced Imaging Techniques: Innovations in imaging will provide even clearer and more detailed visuals.
- AI Integration: Algorithms will allow for quicker and more accurate interpretations of results.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatment options based on comprehensive diagnostic information.
Conclusion: The Importance of Early Detection
The lung cancer CT scan is an invaluable tool in the fight against lung cancer. By facilitating early detection and providing detailed insights into lung health, CT scans play a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes. Whether you’re a patient, healthcare provider, or involved in sports medicine or physical therapy, understanding the significance of lung cancer CT scans is essential in promoting wellness and early intervention. Staying informed and proactive can make all the difference in the realm of health and medicine.
Additional Resources
For more information on lung cancer and CT scans, consider visiting:
- National Cancer Institute
- American Lung Association
- Mayo Clinic